Modular Blockchain Benefits Calculator
Modular Blockchain
Separates consensus, execution, data availability, and settlement into independent layers for enhanced performance and flexibility.
Consensus Execution Data Availability SettlementMonolithic Blockchain
All functions run on a single chain, limiting scalability and upgrade flexibility.
Single LayerBenefit Calculator
Results
Enter values and click Calculate to see the benefits comparison.
Modular vs Monolithic Comparison
| Aspect | Modular Design | Monolithic Design |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Parallel layers enable thousands of TPS | Linear processing limits TPS (e.g., 15-30 TPS) |
| Upgrade Flexibility | Upgrade individual layers without full network fork | Full network upgrades often require hard forks |
| Security Model | Layer-specific audits, isolated attack vectors | Single codebase; a bug can affect the whole chain |
| Interoperability | Built-in cross-chain bridges & IBC-style protocols | Typically isolated, need external bridges |
| Complexity for Developers | Higher learning curve, need to understand layer interactions | Simpler, single stack to learn |
When you hear the term modular blockchain, think of a Lego set for distributed ledgers - each piece does its own job, and together they build something powerful. Traditional blockchains like Bitcoin or early Ethereum try to do everything in one big block, which limits speed and adaptability. By splitting the work into dedicated layers, modular blockchains unlock higher transaction rates, tighter security, and more flexibility without sacrificing decentralization.
What Exactly Is Modular Blockchain Design?
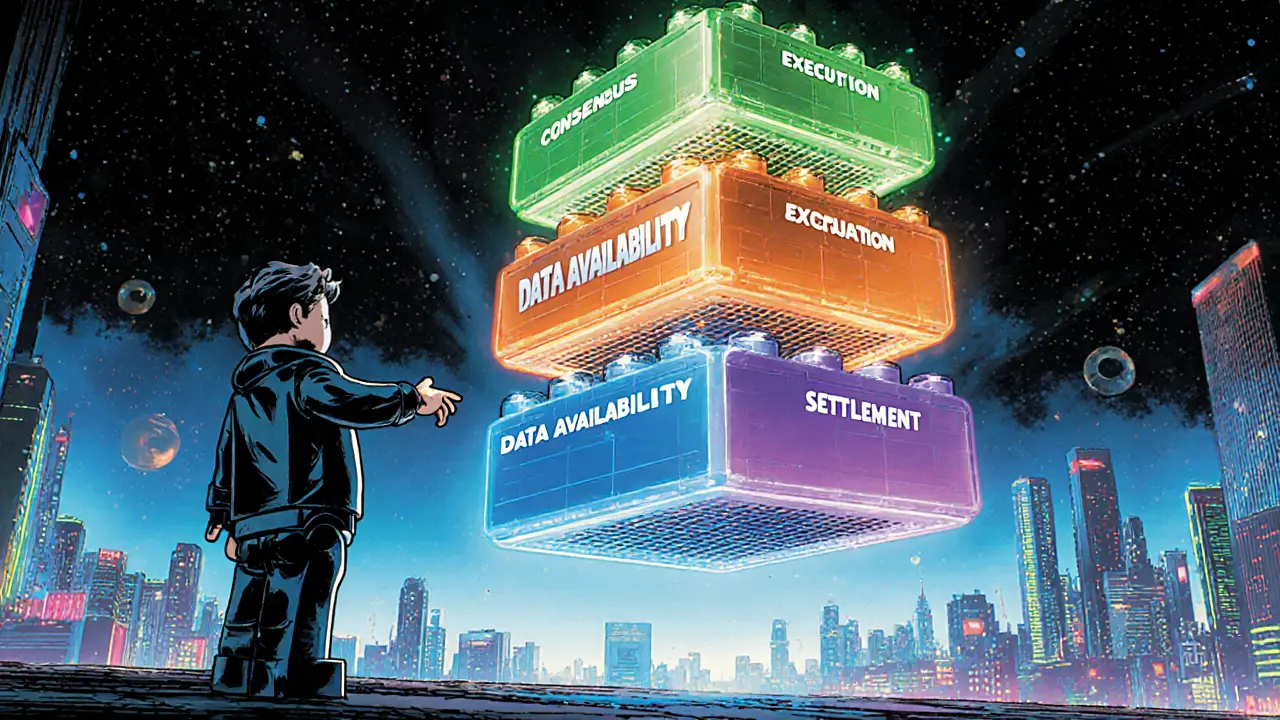
Modular blockchain design is a architectural approach that separates core blockchain functions-consensus, execution, data availability, and settlement-into independent layers. Each layer can be built, upgraded, or replaced without forcing a network‑wide overhaul.
This idea emerged because developers hit a wall with monolithic chains: scaling up meant slower block times, higher fees, or weaker security. By letting layers run in parallel, modular systems aim to solve the classic blockchain trilemma-offering scalability, security, and decentralization together.
How the Layers Fit Together
Think of a modern computer: the CPU, memory, storage, and graphics card each have a specific role. A modular blockchain works the same way.
- Consensus layer validates which blocks are added to the chain. It can use Proof‑of‑Stake, Proof‑of‑Authority, or newer mechanisms without affecting other layers.
- Execution layer runs smart contracts and transaction logic. Projects can pick the virtual machine that suits them-EVM, WASM, or custom runtimes.
- Data availability layer ensures that all necessary data is accessible to validators quickly. By offloading heavy data storage, this layer can use specialized data shards or rollup techniques.
- Settlement layer finalizes transactions and handles cross‑chain transfers. It acts like the final accountant, making sure everything balances before the system records the result.
Because each piece can be optimized on its own, the whole system runs faster and cheaper.
Key Benefits of Going Modular
1. Unmatched Scalability
Parallel processing means the network can handle many more transactions per second (TPS). For example, Polygon’s modular rollup architecture consistently processes >7,000 TPS, far beyond Bitcoin’s 7 TPS.
2. Strengthened Security
When layers are isolated, a vulnerability in the execution layer doesn’t automatically compromise consensus. Teams can audit each component separately, reducing the attack surface.
3. Flexibility and Customization
Developers can choose the best virtual machine for their dApp, swap in a newer consensus algorithm, or add a data‑sharding solution without rebuilding the whole chain.
4. Cost Efficiency
Specialized layers use resources more intelligently. Data‑heavy tasks stay out of the consensus layer, lowering validator hardware requirements and driving down transaction fees.
5. Interoperability Built In
Modular designs often include standardized bridge protocols, making it easier to move assets between chains. Polkadot’s relay chain, for instance, connects dozens of parachains seamlessly.

Real‑World Implementations
The theory isn’t just hype-several live networks prove modular design works.
- Polygon uses a separate rollup (execution) layer on top of Ethereum’s consensus, achieving high throughput and low fees.
- Polkadot separates a central relay chain (consensus) from parachains (execution & data availability).
- Cosmos introduces the Inter‑Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol, letting sovereign zones handle their own consensus while still sharing assets.
These projects illustrate how modularity enables both public and permissioned settings to scale without sacrificing core blockchain principles.
Modular vs. Monolithic: A Quick Comparison
| Aspect | Modular Design | Monolithic Design |
|---|---|---|
| Scalability | Parallel layers enable thousands of TPS | Linear processing limits TPS (e.g., 15‑30 TPS) |
| Upgrade Flexibility | Upgrade individual layers without full network fork | Full network upgrades often require hard forks |
| Security Model | Layer‑specific audits, isolated attack vectors | Single codebase; a bug can affect the whole chain |
| Interoperability | Built‑in cross‑chain bridges & IBC‑style protocols | Typically isolated, need external bridges |
| Complexity for Developers | Higher learning curve, need to understand layer interactions | Simpler, single stack to learn |
While monolithic chains win on simplicity and battle‑testing, modular blockchains win on performance and adaptability.
Challenges You’ll Face
- Steep Learning Curve: Grasping how layers communicate adds extra work for developers.
- Cross‑Layer Latency: Poorly designed interfaces can cause bottlenecks, eroding the speed gains.
- Security Coordination: Each layer may be run by different validator sets, requiring robust governance to avoid inconsistencies.
- Tooling Gaps: Documentation and SDKs are catching up, but they’re not as mature as those for Ethereum or Bitcoin.
Understanding these hurdles early helps you plan resources and avoid nasty surprises.

Getting Started: A Simple Roadmap
- Define Your Use Case - Is high throughput vital? Do you need custom VMs? This determines which layers you’ll prioritize.
- Select a Base Platform - Polygon for rollups, Polkadot for parachains, or Cosmos for independent zones.
- Learn Layer APIs - Study the SDKs for consensus (e.g., Substrate), execution (e.g., Optimistic Rollup), and data availability (e.g., Celestia).
- Prototype a Minimal Viable Product - Build a simple smart contract on the execution layer and test cross‑layer communication.
- Iterate and Optimize - Tweak each layer’s parameters (gas limits, slot times) to hit your performance targets.
After the first prototype, you’ll notice how each layer can be improved independently, shortening future development cycles.
Quick Summary
- Modular blockchain splits consensus, execution, data availability, and settlement into separate, optimizable layers.
- Parallel processing delivers far higher TPS, lower fees, and better resource use.
- Security improves because bugs stay confined to one layer.
- Flexibility lets developers choose VMs, consensus mechanisms, and data solutions that fit their app.
- Real‑world examples - Polygon, Polkadot, Cosmos - prove the model works, though the learning curve is higher than with monolithic chains.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main advantage of modular blockchains over traditional ones?
The biggest win is scalability. By processing consensus, execution, and data availability in parallel, modular chains can handle thousands of transactions per second while still keeping security and decentralization.
Do I need to learn a new programming language to build on a modular blockchain?
Not necessarily. Many modular platforms (e.g., Polygon) still use the Ethereum Virtual Machine, so Solidity works. Others, like Polkadot, support WASM, which lets you write contracts in Rust, C++, or AssemblyScript.
How does security differ between modular and monolithic designs?
In a modular setup each layer can be audited and hardened separately. A flaw in the execution layer won’t automatically compromise the consensus layer, which reduces overall risk.
Can modular blockchains interoperate with each other?
Yes. Protocols like Polkadot’s XCM or Cosmos’ IBC enable seamless asset and data transfers across independent chains that share compatible layers.
What are the biggest challenges when adopting a modular blockchain?
The main hurdles are the steeper learning curve, coordination between multiple validator sets, and less mature tooling compared to legacy monolithic networks.




Leynda Jeane Erwin
October 10 2025Modular blockchains are certainly a hot topic right now. By splitting consensus, execution, data availability, and settlement you get a lot more flexibility. It also means each layer can be upgraded independently, which cuts down on hard forks. Of course, developers need to understand the cross‑layer communication protocols, but the performance gains often outweigh the added complexity.
Siddharth Murugesan
October 12 2025Honestly this modular hype is just a buzzword fad, nobody really needs all those layers.
Nina Hall
October 14 2025Love the way you highlighted real‑world examples like Polygon and Polkadot – it really helps newcomers see the benefits in action. The color‑coded tables make the comparison crystal clear. Keep spreading the good vibes about modular design!
Mureil Stueber
October 16 2025One practical tip: when you’re testing cross‑layer calls, start with a small payload and gradually increase size. This helps you spot latency bottlenecks early without overwhelming the network.
Emily Kondrk
October 18 2025Sure, modularity sounds great until you realize it’s a perfect playground for shadow validators to hide their tracks across layers. The more layers you add, the easier it is to inject subtle backdoors that nobody sees until it’s too late. Stay alert.
Laura Myers
October 20 2025Oh my god, can we talk about how mind‑blowing it is that a single chain can actually be split into multiple “mini‑chains”? It’s like Lego for crypto – you snap pieces together and suddenly you’ve built a whole city! 🚀
Leo McCloskey
October 22 2025While the article is thorough, it glosses over the fact that modular architectures often introduce added inter‑layer latency, which can negate the touted throughput improvements; furthermore, the security assumptions become more complex, demanding rigorous formal verification across each component.
debby martha
October 24 2025I dunno if all this modular stuff is really needed, maybe just stick with what works.
Ted Lucas
October 26 2025🔥 This is exactly why I’m excited about the future of blockchain! Parallel layers mean we can finally get the speed we need for real‑time apps without sacrificing decentralization. Let’s keep the momentum going! 😎
ചഞ്ചൽ അനസൂയ
October 29 2025Think of modular design as a toolbox – pick the right tool for each job. If you need blazing‑fast transaction speeds, focus on the execution layer, but don’t forget the consensus layer’s role in keeping things honest.
Ethan Chambers
October 31 2025One must appreciate the nuanced elegance of decoupling blockchain responsibilities; it is not merely an engineering choice but a philosophical shift towards modular epistemology in distributed systems.
gayle Smith
November 2 2025Listen up, the whole “modular vs monolithic” debate is just the tip of the iceberg – underneath lies a vortex of governance battles, validator economics, and cryptographic intrigue that will define the next era of crypto supremacy.
mark noopa
November 4 2025When contemplating the architecture of a blockchain, one cannot ignore the ontological implications of modularity. Each layer-consensus, execution, data availability, settlement-represents a distinct locus of authority, a compartmentalized micro‑society within the larger network. By isolating these functions, we grant each layer the freedom to evolve independently, much like organs within a living organism adapt to new environments. This separation cultivates resilience; a flaw in the execution layer does not automatically compromise consensus, thereby containing systemic risk. Moreover, parallel processing across layers unlocks throughput potentials that monolithic chains can scarcely imagine, scaling from tens to thousands of transactions per second. Developers are empowered to select specialized virtual machines tailored to their application’s requirements, rather than being shackled to a one‑size‑fits‑all model. Inter‑layer communication protocols, such as IBC or XCM, serve as the circulatory system, transporting data with minimal friction. Yet, this very interconnectivity introduces latency concerns that must be meticulously engineered to avoid bottlenecks. Governance complexities also surface: disparate validator sets governing each layer demand robust coordination mechanisms to prevent forks and misalignments. The security model transitions from a monolithic perimeter defense to a distributed mosaic of audits, each focusing on specific attack vectors. Auditors can concentrate their expertise, performing deep dives into consensus algorithms without being distracted by execution-level bugs. From an economic standpoint, specialized layers enable more efficient resource utilization, reducing hardware requirements for validators and lowering transaction costs for users. However, the learning curve steepens, as engineers must master the intricacies of cross‑layer APIs and state synchronization. In practice, projects like Polkadot, Cosmos, and Polygon demonstrate that these theoretical benefits are attainable, albeit with trade‑offs. Ultimately, modular blockchain design embodies a philosophical evolution toward decentralized modularity, aligning technological architecture with the very principles of autonomy and scalability that the blockchain ethos champions. 🚀
Rama Julianto
November 6 2025Don’t just read the article-actually fork a testnet now and experiment with swapping out the data‑availability layer. You’ll quickly see where the pain points are and can contribute fixes upstream.
Helen Fitzgerald
November 8 2025Hey folks, if you’re new to modular chains, start with a simple roll‑up on Ethereum. It’s a gentle introduction before diving into full‑blown parachains.
Jon Asher
November 10 2025Modular designs let you upgrade parts without breaking everything.
Scott Hall
November 12 2025One thing I’ve noticed is that the community around modular projects tends to be very collaborative, sharing tools and SDKs to lower the entry barrier.
Jade Hibbert
November 14 2025Sure, because adding more layers always makes things easier.
Brandon Salemi
November 16 2025Modular chains are the future, period.
hrishchika Kumar
November 18 2025The vibrant ecosystems blossoming around modular frameworks remind me of a bustling marketplace, each stall offering a unique protocol flavor that enriches the whole experience.
Lena Vega
November 20 2025Keep the modular approach simple.
Nathan Van Myall
November 23 2025I wonder how cross‑layer governance will evolve as more independent validators join each tier.
Daron Stenvold
November 25 2025It is both exhilarating and daunting to witness the paradigm shift toward compartmentalized blockchain structures, heralding a new epoch of scalability and robustness.
Manas Patil
November 27 2025From a strategic standpoint, modularity empowers enterprises to adopt a plug‑and‑play model, integrating best‑in‑class consensus mechanisms while retaining legacy compliance layers.
Jacob Moore
November 29 2025Happy to see more developers sharing their modular experiments-let’s keep the knowledge flowing!